Biceps Brachii: In-Depth Look at this Powerful Muscle
The biceps brachii, commonly known as the biceps, is a two-headed muscle located on the front of the upper arm.
This muscle plays a crucial role in arm movements, particularly flexion and supination. Its distinctive appearance and functional significance have made it an iconic muscle in the realm of fitness and strength training.
Anatomical Structure
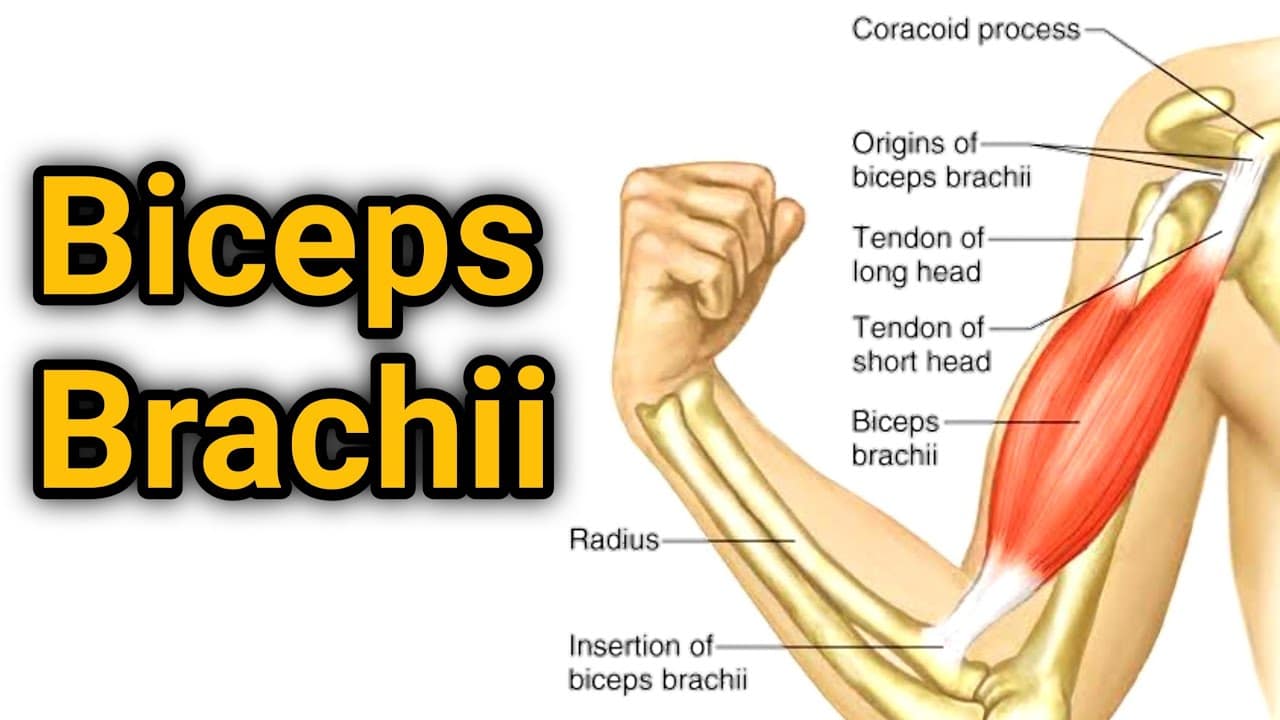
The biceps brachii is a fusiform muscle, meaning it has a spindle-like shape with a thick belly in the middle and tapered ends.
It consists of two heads, aptly named the short head and the long head.
The short head of the biceps brachii originates from the coracoid process of the scapula (shoulder blade).
This attachment point is located near the shoulder joint. The long head, on the other hand, originates from the supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula, situated within the shoulder joint capsule.
Both heads converge and form a single muscle belly, which extends down the front of the upper arm.
The muscle belly then transitions into a strong tendon that inserts into the radial tuberosity, a bony protrusion located on the radius bone of the forearm.
Muscle Innervation and Blood Supply
The biceps brachii is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve, a branch of the brachial plexus.
This nerve provides motor innervation, allowing the muscle to contract and generate movement.
The brachial artery, a major artery in the upper arm, supplies oxygenated blood to the biceps brachii.
It is accompanied by the venae comitantes, which are a pair of veins responsible for draining deoxygenated blood from the muscle.
Functions and Actions ( Biceps Brachii: In-Depth Look at this Powerful Muscle )
The primary function of the biceps brachii is to flex the elbow joint, allowing the forearm to move towards the upper arm.
This action is crucial for activities such as lifting weights, pulling objects, and performing various daily tasks that require arm flexion.
Additionally, the biceps brachii plays a role in supination, which is the rotation of the forearm and hand to a palm-up position.
This action is facilitated by the long head of the biceps, as it crosses the shoulder joint and exerts a rotational force on the radius bone.
The biceps brachii also assists in shoulder flexion and abduction (raising the arm away from the body) when the elbow is extended.
However, it is important to note that the primary movers for these shoulder movements are the deltoid and rotator cuff muscles.
Training and Strengthening
The biceps brachii is a highly visible muscle, and its development is often a goal for many fitness enthusiasts and athletes.
Exercises that target the biceps brachii include:
- Biceps Curls: This exercise involves flexing the elbow joint by lifting a weight (dumbbell or barbell) towards the shoulder. Variations include standing biceps curls, seated biceps curls, and preacher curls.
- Hammer Curls: Similar to biceps curls, but with a neutral grip (palms facing inward), this exercise emphasizes the brachialis muscle in addition to the biceps brachii.
- Chin-ups and Pull-ups: These compound exercises engage the biceps brachii as a secondary mover, helping to flex the elbow and assist in pulling the body up towards the bar.
- Rows: Exercises like bent-over rows and seated cable rows involve rowing motions that engage the biceps brachii as a synergist muscle.
Proper form and technique are crucial when training the biceps brachii to ensure safety and maximize muscle activation.
It is also important to incorporate a balanced training regimen that targets all major muscle groups for overall strength and muscular development.
Injuries and Conditions
Despite its strength, the biceps brachii is susceptible to various injuries and conditions:
- Biceps Tendinitis: Inflammation of the biceps tendon, often caused by overuse or repetitive stress, can lead to pain and discomfort during arm movements.
- Biceps Tendon Rupture: A complete or partial tear of the biceps tendon can occur due to traumatic injuries or chronic degeneration. This injury often results in a significant loss of strength and a visible deformity in the arm.
- Muscle Strains: Excessive or sudden loading on the biceps brachii can lead to muscle strains, characterized by pain, swelling, and reduced range of motion.
- Compartment Syndrome: In rare cases, excessive muscle swelling within the confined compartments of the upper arm can lead to increased pressure and potential nerve damage, a condition known as compartment syndrome.
Proper warm-up, gradual progression, and appropriate rest are essential for preventing injuries and maintaining the health and function of the biceps brachii.
Conclusion ( Biceps Brachii: In-Depth Look at this Powerful Muscle )
The biceps brachii is a remarkable muscle that not only contributes to the aesthetics of the upper arm
But also plays a vital role in various arm movements. Its two-headed structure, innervation, and blood supply work in harmony to provide strength and flexibility for daily activities and athletic endeavors.
Understanding the anatomy and function of the biceps brachii is crucial for athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and healthcare professionals alike, as it helps optimize training, prevent injuries and address any potential conditions affecting this iconic muscle.

Dr. Shabbir Hussain Bohra (Physio)
Owner & Founder – Physio Talk
Director – HAKIMI Physiotherapy Clinic, Nagpur
Dr. Shabbir Hussain Bohra is a dedicated physiotherapist with seven years of comprehensive experience in rehabilitation and specialized therapeutic care. He holds a Bachelor of Physiotherapy (BPT) degree and has established himself as a leading expert in oncology physiotherapy and lymphedema management. Currently serving as a Consultant Physiotherapist at Asian Kidney Hospital, Nagpur, director hakimi Physiotherapy clinic nagpur Dr. Bohra brings extensive expertise in treating complex medical conditions requiring specialized rehabilitation approaches. His dual specialization as an Onco-Physiotherapist and Lymphedema Therapist enables him to provide targeted care for cancer patients and individuals managing lymphatic disorders.