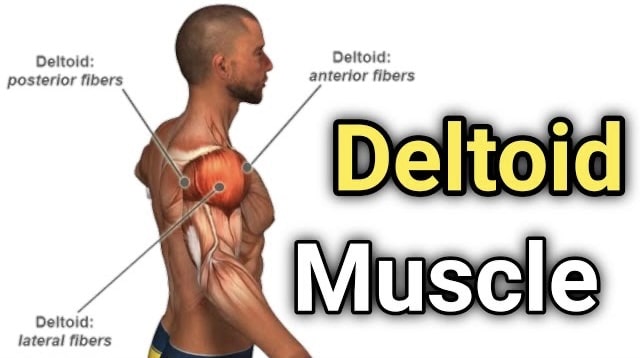
The deltoid muscle, commonly referred to as the deltoid, is a large triangular muscle located in the shoulder.
It is named after its delta-like shape, resembling the Greek letter “delta” (∆).
The muscle is responsible for the majority of the movements of the shoulder joint.
Deltoid Parts / Sections
The muscle has three distinct sections or heads: anterior (front), middle, and posterior (back).
Each head has specific functions and contributes to different movements of the shoulder.
Anterior head:
The anterior head of the muscle is located at the front of the shoulder.
It is involved in shoulder flexion, which is the movement of raising the arm forward, as well as internal rotation of the arm.
Middle head:
The middle head of the muscle is located in the central part of the shoulder.
It plays a significant role in shoulder abduction, which is the movement of raising the arm to the side away from the body.
It is the main muscle responsible for lateral or side arm raises.
Posterior head:
The posterior head of the muscle is located at the back of the shoulder.
It assists in shoulder extension, which is the movement of pulling the arm backward, as well as external rotation of the arm.
Deltoid Movement
Overall, the deltoid muscle is crucial for various movements of the shoulder, including lifting, rotating, and moving the arm in different directions.
It works in conjunction with other muscles, such as the rotator cuff muscles, to provide stability and facilitate smooth shoulder movements.
Deltoid Muscle Functions
Certainly! In addition to its primary functions, the muscle also plays a role in stabilizing the shoulder joint during various movements.
It works together with other muscles, such as the rotator cuff muscles (including the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis).
To provide dynamic stability and prevent dislocation or excessive movement of the shoulder.
Deltoid muscle innervation
The muscle is innervated by the axillary nerve, which arises from the brachial plexus in the neck.
This nerve supplies motor signals to the muscle, enabling it to contract and produce movement.
Sensory information from the deltoid region is also transmitted through the axillary nerve.
Exercise to keep Deltoid Muscle strong
To keep the muscle strong and functional, exercises that target its different heads are commonly advice
These exercises may include shoulder presses, lateral raises, front raises, upright rows, and various forms of arm abduction and rotation.
Strengthening the deltoids can help improve shoulder stability, enhance overall upper body strength, and support activities that involve overhead movements.
Injury to Deltoid Muscle
It is important to note that injuries to the deltoid muscle, such as strains or tears, can occur due to overuse, trauma, or improper technique during exercises.
In such cases, rest, physical therapy, and sometimes surgical intervention will be require for recovery.
Overall, the deltoid muscle is a vital component of the shoulder complex.
enabling a wide range of movements and contributing to the overall function and stability of the shoulder joint.
Some Additional Information about Deltoid
Certainly! Here’s some additional information about the deltoid muscle:
The deltoid muscle receives its blood supply from various arteries, including the posterior circumflex humeral artery, thoracoacromial artery, and deltoid branches of the thoracoacromial artery.
These arteries ensure that the muscle receives an adequate oxygen and nutrient supply for its proper function.
The deltoid muscle is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the deltoid fascia.
This fascia helps to support and protect the muscle, as well as provide a structural framework for its attachment to the clavicle (collarbone), acromion process of the scapula (shoulder blade), and the spine of the scapula.
The deltoid muscle is highly visible and contributes to the overall aesthetic appearance of the shoulder region.
Well-developed deltoid muscles are often associate with a V-shaped upper body and are a common focus in strength training and bodybuilding exercises.
Injuries to the deltoid muscle can range from mild strains to more severe tears.
Deltoid injury Symptoms
Symptoms of a deltoid muscle injury may include pain, weakness, swelling, and limited range of motion in the shoulder.
Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) are commonly recommend for initial treatment, followed by physical therapy to restore strength and flexibility.
It is worth noting that while the deltoid muscle is primarily responsible for shoulder movements, other muscles in the upper body, such as the pectoralis major, trapezius, and rotator cuff muscles, also contribute to shoulder stability and motion.
Overall, the deltoid muscle is a powerful and important muscle of the shoulder, enabling a wide range of movements and providing stability to the shoulder joint.
Its proper functioning is crucial for activities that involve arm movements, such as lifting, throwing, pushing, and pulling.
Click here to read our intresting articles on femur anatomy