Painful arc syndrome ?
What is Painful arc syndrome – “Painful arc syndrome” refers to a condition characterized by shoulder pain during specific movements or ranges of motion.
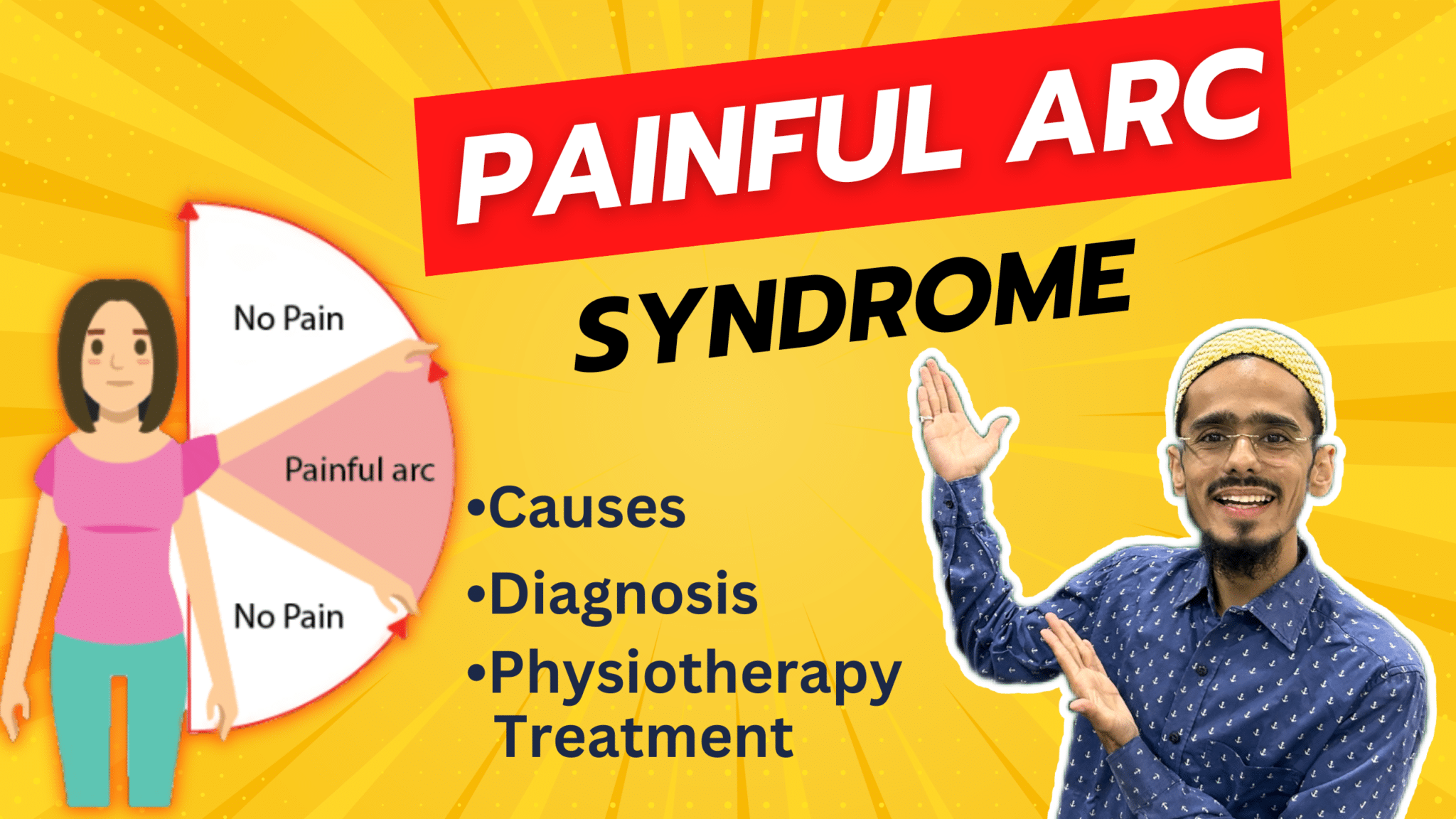
Typically this syndrome manifests as pain or discomfort when lifting the arm out to the side and upwards, specifically between 60 to 120 degrees of shoulder abduction.
The pain may be sharp, achy, or even a feeling of catching or grinding within the shoulder joint.
The most common cause of painful arc syndrome is impingement of the structures within the shoulder joint, such as the rotator cuff tendons or the bursa.
When the arm is lifted, these structures can become compressed or pinched between the bones of the shoulder, leading to pain.
Several factors can contribute to the development of painful arc
Causes of painful arc syndrome
Painful arc syndrome, or painful arc of shoulder abduction, can have several potential causes.
Shoulder impingement:
The most common cause of painful arc syndrome is shoulder impingement.
It occurs when the tendons of the rotator cuff or the subacromial bursa become compressed or pinched between the bones of the shoulder joint particularly the acromion and the humeral head.
Rotator cuff tendinitis or tear:
Inflammation or tearing of the rotator cuff tendons, which are responsible for stabilizing the shoulder joint can lead to painful arc syndrome.
Repetitive overhead activities or trauma to the shoulder can contribute to rotator cuff injuries.
Shoulder bursitis:
The subacromial bursa is a fluid-filled sac that helps reduce friction between tendons and bones in the shoulder joint.
Inflammation or irritation of the bursa, known as bursitis, can result in painful arc syndrome.
Shoulder instability:
Instability of the shoulder joint, which can occur due to ligament laxity or previous dislocations can cause abnormal movement patterns and lead to impingement and pain during shoulder abduction.
Muscle imbalances or weakness:
Weakness or imbalances in the muscles around the shoulder, particularly the rotator cuff muscles and the scapular stabilizers can contribute to abnormal shoulder mechanics and increase the risk of this condition
Overuse or repetitive strain:
Engaging in repetitive overhead activities, such as throwing, swimming or lifting weights improperly, can put excessive stress on the shoulder joint and lead to painful arc syndrome over time.
painfull arc syndrome diagnostic tests
Here are some diagnostic tests that may be used in the evaluation of painful arc syndrome:
Physical Examination: painful arc test
A healthcare provider will assess your shoulder by examining its range of motion, strength, and stability. They may also palpate specific areas to identify tender spots or signs of inflammation.
Medical History: painful arc shoulder
Your healthcare provider will ask you questions about your symptoms, such as the location and duration of pain, activities that exacerbate or relieve the pain, and any previous shoulder injuries.
X-rays:
X-rays are commonly used to evaluate the bony structures of the shoulder joint. They can help identify abnormalities such as bone spurs, fractures, or joint degeneration.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging):
An MRI provides detailed images of the soft tissues, including muscles, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage. It can help identify issues such as rotator cuff tears, inflammation, or other structural abnormalities.
Ultrasound:
Ultrasound imaging uses sound waves to create real-time images of the shoulder joint. It is often used to evaluate the condition of tendons, muscles, and other soft tissues.
CT Scan (Computed Tomography):
A CT scan may be used in cases where detailed imaging of the bones or joints is necessary. It provides cross-sectional images that can help assess bone abnormalities or evaluate complex fractures.
It’s important to remember that the specific diagnostic tests recommended for this condition may vary depending on individual circumstances and the judgment of the healthcare professional.
Therefore, it is crucial to consult with a qualified Doctor for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Painful arc syndrome Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy can be an effective treatment approach for individuals with painful arc syndrome.
A physiotherapist will work with you to reduce pain, improve shoulder mobility, and strengthen the muscles around the shoulder joint.
Here are some common physiotherapy interventions
Range of motion exercises:
Your physiotherapist may guide you through specific exercises to improve the range of motion in your shoulder joint. Like pendulum exercises, wall slides, or shoulder circles.
Stretching exercises:
Stretching can help improve flexibility and relieve muscle tension around the shoulder. Your physiotherapist may teach you stretches targeting the muscles involved in painful arc syndrome, such as the rotator cuff and the muscles around the shoulder blade.
Strengthening exercises:
Strengthening exercises are essential for improving the stability of the shoulder joint.
Your physiotherapist will design a program that targets the muscles which supports the shoulder, including the rotator cuff muscles, deltoids, and scapular stabilizers.
These exercises may involve resistance bands, weights or bodyweight exercises.
Manual therapy:
Your physiotherapist may use various hands-on techniques to help reduce pain and improve shoulder mobility. Manual therapy techniques can include joint mobilization, soft tissue mobilization and trigger point release.
Posture correction:
Poor posture can contribute to shoulder impingement and painful arc syndrome.
Your physiotherapist can assess your posture and exercises to improve alignment and reduce strain on the shoulder joint.
Modalities:
Depending on your symptoms, your physiotherapist may use modalities such as ice or heat therapy, ultrasound or electrical stimulation to help manage pain, reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Education and self-management:
Your physiotherapist will educate you about proper shoulder mechanics, ergonomics, and activity modification techniques to avoid aggravating the condition.
They may also provide guidance on home exercises and self-management strategies to support your recovery.
It is important to work closely with a qualified physiotherapist who can tailor the treatment plan to your specific needs.
They will monitor your progress adjust the exercises as necessary and provide guidance to ensure a safe and effective rehabilitation process.
1 thought on “Painful arc syndrome ?”
Comments are closed.